Fatty Liver : Your Questions; My Answers
Fatty liver related disease; Your questions: My answers
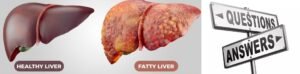
Q 1 . How common is fatty liver related liver disease ?
In India, the prevalence of fatty liver related disease in the general population varies from 9 to 53%. The prevalence among patients with diabetes mellitus was reported to be 56.5%.
Q 2. Can fatty liver disease run in families ? Genetic? Hereditary?
Yes. Certain genetic disorders and mutation can run in family. These can lead to fatty liver related diseases.
Q 3. Is fatty liver common in children?
Yes
The prevalence of 12.4% to 63.4% Indian children
Q 4. Which children should be screened for fatty liver related diseases ?
The screening with blood report
1.Obese children above 9 years of age
2.Overweight children with family history of NAFLD or other risk factors.
Q 5. What are the stages of fatty liver related disease?
It can be categorised in 3 broad stages Fatty liver, Non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) , cirrhosis
Q 6. What is NASH?
NASH has fatty liver with hepatic inflammation and or fibrosis
Q 7. What is lean NASH? Can fatty liver disease happen to thin individuals?
Around 10–20% of patients with fatty liver related disease may have normal body mass index and normal waist circumference.
Q 8. What do I feel in fatty liver disease ? Is fatty liver painful? Does fatty liver cause gas?
Generally there are no symptoms. Some patients may feel fatigue, weakness. In advanced liver disease / cirrhosis patient may develop fluid in tummy, leg swellings, jaundice, gas related issues.
Q 9. What is the reason for fatty liver disease ? What is the main cause of a fatty liver?
When fat accumulates in liver beyond certain limit it start affecting liver functions and causing damages. Excess calorie consumption than required is main reason.
Q 10. What food causes fatty liver disease? Which food is harmful for liver?
Weight gain is most important reason. Junk or high calorie diet like fast food , samosa, sweet’s, Wada pav, juices, soft drinks, alcohol, refined sugars, saturated fat.
Q 11. Which individuals should be screened for fatty liver related diseases?
- Overweight and obese individuals
- Patients with DM, Obesity ,Metabolic syndrome, PCOS
Q 12. Which other organs affected by fatty liver related disease?
Other disease associated with fatty liver related disease are Heart disease , kidney disease, bone related issues like osteopenia and osteoporosis, PCOS, stroke, hormone related issues like hypothyroidism, obstructive sleep apnoea.
Q 13. Is there increased risk of cancers in fatty liver diseases?
Yes. There is increased risk of HCC, carcinoma colon, gastric cancer, carcinoma pancreas, uterine and breast carcinoma.
Q 14. How much time to develop advance disease in fatty liver related disorder ? Is fatty liver serious problem? Can I live with a fatty liver?
It depends upon present state of liver. This can be known with the help of fibroscan.
Time to development of advanced liver disease is
22–26 years in F0-1 fibrosis
9.3 years in F2 fibrosis
2.3 years in F3 fibrosis
Q 15. What blood tests show fatty liver? Does fatty liver show in LFT?
Fatty liver is shown on ultrasound. Blood tests help to assess the fatty liver related injury to liver.
Q 16. What is Stage 1 fatty liver?
Ultrasound will detect fatty liver and categorised it into 3 grades, Fatty liver 1,2 and
- It depends upon amount of fat deposition in liver. Grade 1 Fatty liver has less fat
deposition in liver than grade 3. It does not necessarily mean Fatty liver grade 3 is
more severe form than grade 1.
Q 17. Which is good available non-invasive test to detect permanent or chronic liver damage?
Fibroscan , MR elastography, ARFI
Q 18. How do I manage fatty liver related diseases? How to reduce my fatty liver ? Can fatty liver be cured? What is the fastest way to cure a fatty liver? How can I normalize my fatty liver naturally? How long does fatty liver take to heal?
Yes in early fatty liver disease with mild inflammation and mild fibrosis can be cured over months with right approach but advanced fatty liver related disease has to be controlled, it is in sense damage control mode approach. Following are the ways,
- Risk factor modification: overweight or obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
- Weight reduction 10% through diet , lifestyle exercise, Exercise . brisk walking, jogging, running, swimming, or cycling for 30–45 min/day at least 5 days in a week (at least 200 min per week) to achieve a target heart rate of 60–70% of maximal heart rate.
- Medication : saroglitazar, Vit E , obetocholic acid, semaglutide , liraglutide.
- Bariatric surgery and endoscopic Bariatric procedure
Q 19. Which diet or fruit is best for fatty liver ? Which fruit is best for liver?
Low calorie and adequate protein diet. So no particular food types are best. Final goal is to reduce weight and build muscle mass. High fiber diet, vegetables, fruits should be included in diet.
Q 20. Which exercises are good for fatty liver ?
Aerobic and muscle strengthening exercises are important. Good muscle mass replaces some of the liver related functions and gives rest to liver. Also poor muscle mass is poor prognostic factor in liver disease.
Q 21. Will lean NASH patient benefit with weight loss or exercise ?
Yes.
exercise improves insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis even without weight loss.
